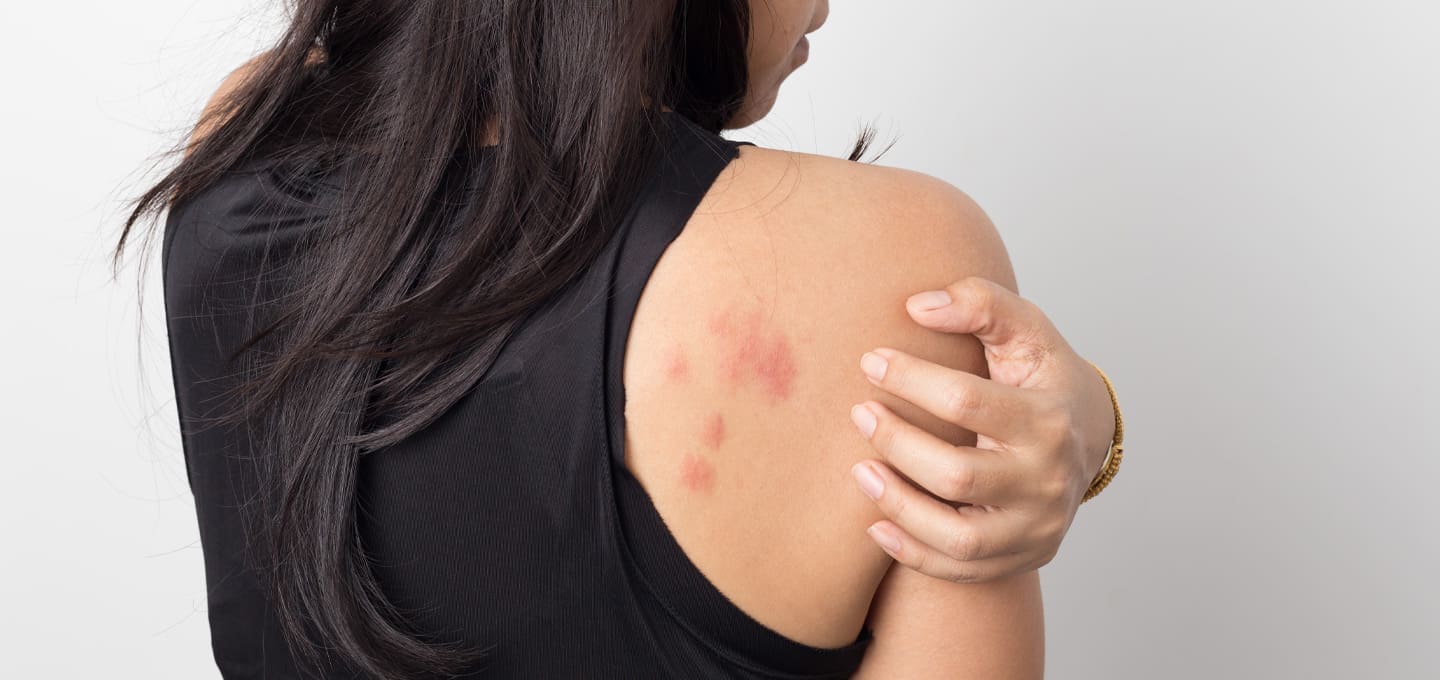
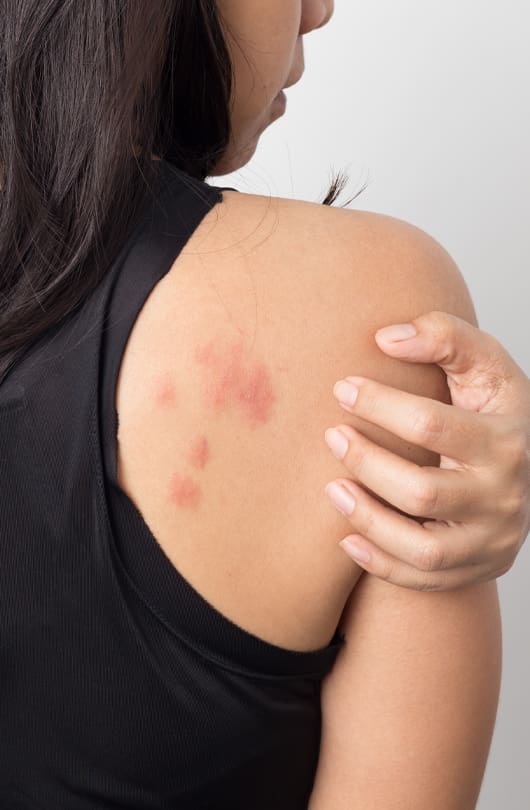
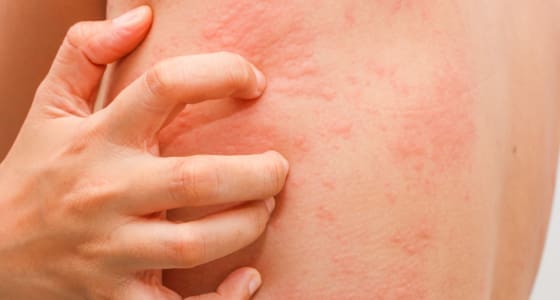
These welts can vary in size and shape and often appear suddenly. Urticaria occurs due to the release of histamines and other inflammatory substances in the skin, causing localised swelling and itching.
There are two main types of urticaria: acute and chronic. Acute urticaria typically lasts for a few hours to several days and is often triggered by allergic reactions to substances like certain foods, medications, insect stings, or contact with irritants. Chronic urticaria, on the other hand, persists for six weeks or longer and can be more challenging to identify the specific triggers. It may be linked to underlying health conditions, autoimmune disorders, or sometimes has no identifiable cause.
The causes of urticaria can be diverse. In addition to allergies, it can be triggered by stress, infections, hormonal changes, or physical factors like pressure, heat, or cold. Some individuals may be prone to chronic urticaria due to autoimmune factors, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the skin.
Treatment for urticaria aims to relieve symptoms and, when possible, identify and address the underlying cause. Antihistamines, both over-the-counter and prescription-strength, are commonly used to block histamine receptors and alleviate itching and swelling. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
Avoiding known triggers is crucial for preventing future outbreaks. Lifestyle modifications, such as stress management techniques, can also be beneficial for individuals with chronic urticaria. In cases where the cause remains elusive or treatment is not effective, further evaluation during a dermatology consultation by one The Day Clinic’s consultant dermatologists may be necessary.
It’s important for individuals experiencing urticaria to consult with our trained medical professionals to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the type, severity, and underlying causes of their condition.